Understanding of SFP and CFP Transceiver Modules.
Where what are they, where and why?
SFP. Small Form-factor Pluggable transceiver
SFP. Small Form-factor Pluggable is a type of transceiver module used for high-speed data transfer in networking applications. It is called “small form-factor” because it is compact and designed to fit into small form-factor switches, routers, and other network equipment.
SFP transceiver modules are used to provide a variety of networking capabilities, including Gigabit Ethernet, Fiber Channel, and various WDM (Wavelength Division Multiplexing) technologies. They can be used for both short-reach and long-haul connections, depending on the type of SFP module and the wavelength of the optical signal being transmitted.
SFP transceiver modules are designed to be hot-swappable, which means that they can be easily inserted or removed from the network equipment without disrupting the network. This allows for easy upgrades and maintenance without affecting network availability.
SFP transceiver modules provide several benefits over traditional transceiver technologies, including increased port density, lower power consumption, and higher reliability. They are also highly standardized, allowing for compatibility and interoperability between different vendor’s equipment.
In conclusion, SFP transceiver modules are an important component of modern networks, providing a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solution for transmitting and receiving high-speed data.
In a networking setup, the SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) transceiver module performs the media conversion, while the switch or router provides the interface for the SFP module.
The SFP module is responsible for converting the electrical signals from the switch or router into optical signals that can be transmitted over a fiber optic cable. The SFP module then receives the optical signals from the fiber optic cable and converts them back into electrical signals that can be processed by the switch or router.
The switch or router provides the SFP module with the electrical signals to be transmitted, as well as the power required to operate the SFP module. The switch or router also provides the interface for the SFP module, allowing it to be easily inserted or removed as needed.
In this setup, the SFP module acts as a “bridge” between the electrical signals of the switch or router and the optical signals of the fiber optic cable. The SFP module enables the switch or router to transmit data over long distances, making it an essential component for many high-speed networking applications.

CFP. C Form factor Pluggable transceiver
CFP. C Form-factor Pluggable transceiver modules are devices that transmit and receive high-speed optical signals for use in data centres and other networking applications. They are designed to be inserted into the CFP port of network switches, routers, and other network equipment.
CFP transceiver modules are used to provide a high-speed, long-haul interconnect between data centres, buildings, and other network elements. They are commonly used for 100 Gigabit Ethernet (100 GbE) and 400 Gigabit Ethernet (400 GbE) networks, which require high bandwidth and low latency to support the growth of data-intensive applications such as cloud computing, big data analytics, and high-definition video streaming.
CFP transceiver modules are highly standardized and are designed to meet industry specifications set by organizations such as the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) and the Optical Internetworking Forum (OIF). These specifications ensure compatibility and interoperability between different vendors’ equipment, allowing for seamless integration and easy upgrades.
CFP transceiver modules offer several benefits over traditional transceiver technologies, such as SFP+ (Small Form-factor Pluggable) and XFP (10 Gigabit Small Form-factor Pluggable). They provide a higher density of ports per line card, allowing for greater scalability and cost-effectiveness in network equipment. They also offer a lower power consumption and higher reliability, which helps to reduce operating expenses and improve network uptime.
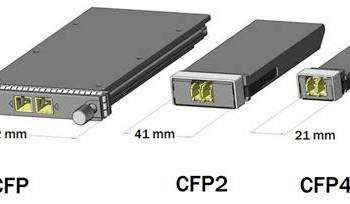
In conclusion, CFP transceiver modules are an essential component of modern high-speed networks, providing a flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solution for transmitting and receiving high-speed optical signals.

